Hypertrophic scars are an abnormal response to the wound healing process that results in excessive scar tissue formation. These scars can be raised, thick, and red, and they can cause discomfort, itching, and even restrict movement in severe cases. In this article, we will explore the causes, appearance, and treatment options for hypertrophic scars.

Causes of Hypertrophic Scars
Hypertrophic scars are caused by an overproduction of collagen during the healing process. Collagen is a protein that is a key component of the extracellular matrix of connective tissues in the body. In normal wound healing, the body produces just enough collagen to repair the damaged tissue. However, in hypertrophic scarring, the body produces an excess of collagen, leading to the formation of a thick, raised scar.
Certain factors can increase the risk of developing hypertrophic scars. These include:
Genetics: Some people may be more prone to developing hypertrophic scars due to genetic factors.
Wound location: Areas with a higher concentration of tension or movement, such as the shoulders or back, are more prone to developing hypertrophic scars.
Wound severity: Deep wounds, burns, and surgical incisions are more likely to result in hypertrophic scarring.
Infection: Infections in a wound can prolong the healing process and increase the risk of hypertrophic scarring.
Appearance of Hypertrophic Scars
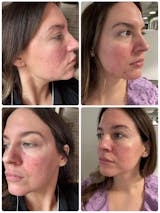
Hypertrophic scars are raised, thick, and red or pink in color. They can be smooth or textured and may cause discomfort, itching, or pain. These scars can appear anywhere on the body, but are most commonly found on the chest, back, and shoulders.
It is important to differentiate between hypertrophic scars and keloid scars, as they are often mistaken for each other. Keloid scars are similar to hypertrophic scars in that they are raised and thick, but they extend beyond the boundaries of the original wound and can continue to grow over time. Hypertrophic scars, on the other hand, are confined to the area of the original wound.
How to Treat Hypertrophic Scars
There are several treatment options for hypertrophic scars, but it is important to note that there is no one-size-fits-all approach. The choice of treatment will depend on the severity and location of the scar, as well as the individual's overall health and medical history.
Silicone sheets/gels: These are non-invasive treatments that involve applying silicone sheets or gels to the scar for a few hours each day. This treatment can help to reduce redness, itching, and discomfort, and may help to flatten the scar over time.
Corticosteroid injections: This treatment involves injecting a corticosteroid medication directly into the scar tissue. Corticosteroids work by reducing inflammation and suppressing the immune system, which can help to reduce the size and thickness of the scar.
Laser therapy: Laser therapy is a non-invasive treatment that uses intense bursts of light to break down scar tissue. This treatment can help to reduce redness and improve the texture of the scar.
Surgical excision: Surgical excision involves removing the hypertrophic scar tissue entirely. This treatment may be recommended for large or severe scars that are causing discomfort or restricting movement. However, there is a risk of the scar returning after surgery, and the procedure itself may result in further scarring.
Cryotherapy: Cryotherapy involves freezing the scar tissue with liquid nitrogen, causing the tissue to die and fall off. This treatment may be effective for small hypertrophic scars, but it may not be suitable for larger scars.
Pressure therapy: This treatment involves applying pressure to the scar tissue with compression garments or bandages. This treatment can help to reduce the size and thickness of the scar over time.